Spinal Health with Expert Spinal Mobilizations
Elevate Your Spinal Health with Advanced Spinal Mobilizations
Welcome to DC Physiotherapy Clondalkin Dublin, where we specialize in providing expert physiotherapy services, including the transformative practice of spinal mobilizations. If you're seeking relief from spinal pain, stiffness, or reduced mobility, our skilled practitioners are here to guide you on a journey to optimal spinal health.
Generally, back pain is caused mainly by any region within the lumbar spine getting nervous system intervention. Thus, back pain arises from muscles, the lumbar spine’s disc, fascia, or any ligaments.
Understanding Spinal Mobilizations
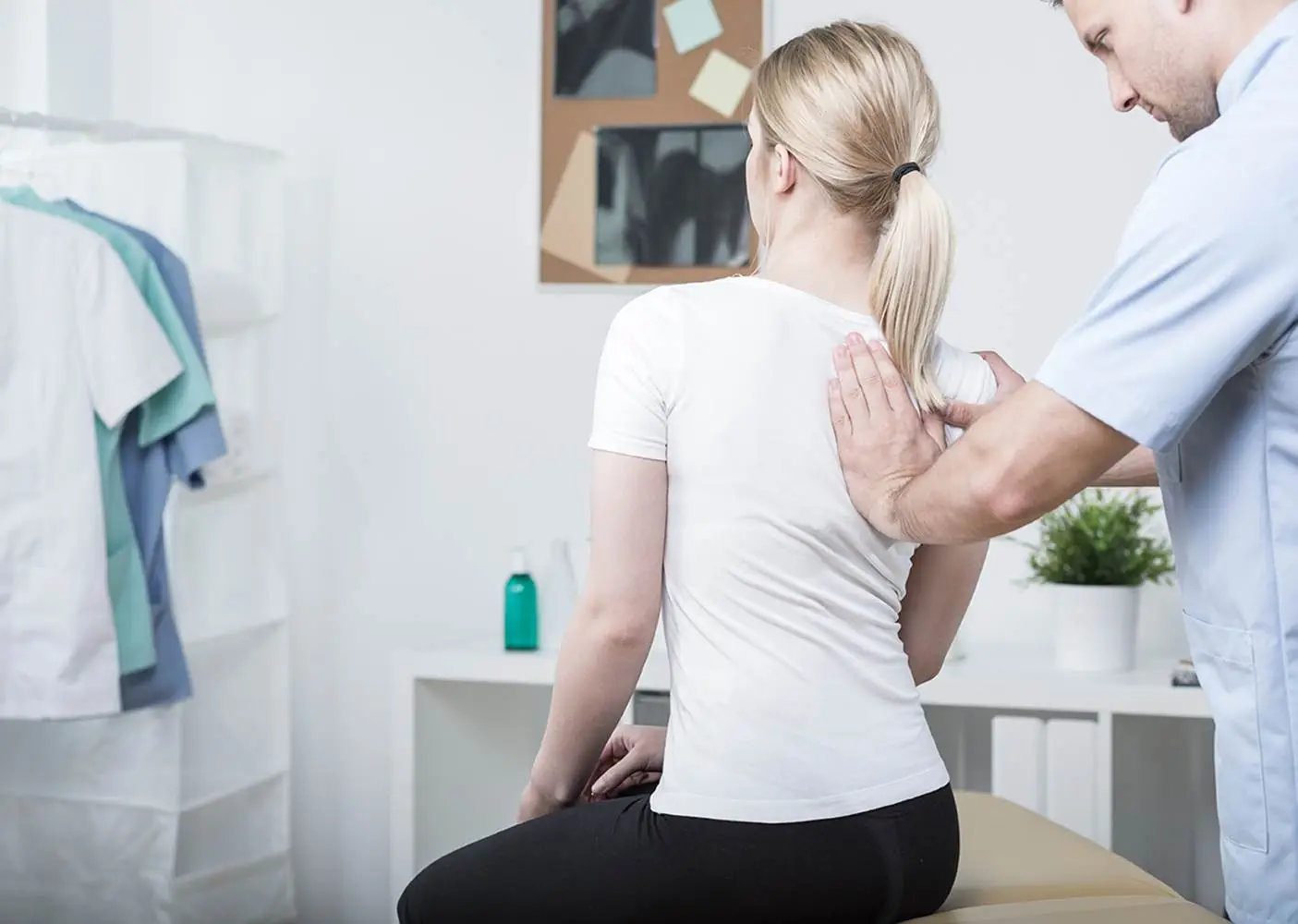
Unlocking Flexibility and Comfort: Spinal mobilizations are a specialized physiotherapy technique aimed at improving the range of motion and flexibility of the spine. Whether you're dealing with chronic back pain, stiffness, or issues related to posture, our practitioners utilize targeted movements to gently mobilize the vertebrae, promoting a healthier and more functional spine.
Personalized Assessment for Tailored Treatment: At DC Physiotherapy Clondalkin Dublin, we understand that each individual's spinal health is unique. Our experienced physiotherapists begin with a thorough assessment to identify specific areas of concern and develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses your unique needs and goals.
Our Approach to Spinal Mobilizations
1. Targeted Techniques: Our skilled practitioners use a variety of specialized techniques to mobilize the spine. These may include gentle stretches, controlled movements, and manual adjustments to specific vertebrae. These targeted techniques are designed to alleviate tension, improve flexibility, and reduce pain.
2. Pain Management and Symptom Relief: Spinal mobilizations play a crucial role in pain management. By addressing the root causes of spinal discomfort, our treatments aim to provide immediate relief and create a foundation for long-term spinal well-being.
3. Improved Posture and Functionality: Beyond pain relief, spinal mobilizations contribute to improved posture and functionality. Whether you're recovering from an injury or looking to enhance your overall spinal health, these treatments support a more aligned and balanced spine.
Why Choose DC Physiotherapy Clondalkin Dublin for Spinal Mobilizations?
- Expert Practitioners: Our team comprises skilled physiotherapists with specialized training in spinal mobilizations, ensuring that you receive the highest standard of care.
- Collaborative Care: We work closely with you to understand your concerns, preferences, and goals, creating a collaborative environment for your optimal well-being.
- Holistic Approach: Our physiotherapy services go beyond addressing symptoms; we take a holistic approach to promote overall spinal health and prevent future issues.
Take the First Step Towards Optimal Spinal Health
Ready to experience the transformative benefits of spinal mobilizations? Schedule a consultation with [Your Clinic Name] and let our skilled practitioners guide you on a personalized journey towards a healthier, more flexible, and pain-free spine.
Contact us today to book your appointment and elevate your spinal health with expert care.
Mobilisations
Spinal Mobilisation is a form of Manual Therapy. It helps to relieve pressure on joints and reduce inflammation. It aims to provide short term or long term pain relief. It also helps to restore the functional movements of the joint. Passive movements define mobilisation and are also known as accessory or physiological.
Joint mobilisation restores the joint’s function and helps to manage musculoskeletal dysfunction. It improves the restricted movements of the spine. Muscles, connective tissues and the joints are prone to such restrictions, causing pain. Mobilisation removes this restriction, giving relief from pain. A deeper and forceful mobilisation can help in decreasing the stiffness in joints. This technique is also known as Manual Therapy, and physiotherapists perform it.
Effects & Mechanism
Research indicated that manual therapy results in significant neurophysiological and mechanical effects. The exact mechanism of mobilisation and needs further research. The effects produced by the manual therapy, however, such as the effects on the autonomic nervous system, motion range increase, and pain relief, suggest alternate theories.